Writing a university assignment might seem overwhelming, but if you break it into smaller steps, you can create a clear, well-organized final piece. This blog will walk you through the important points that will help you in coming up with well-structured and impactful assignments. It will assist you how to write a university assignment to secure better performance.
Structure of a University Assignment
University assignment is usually determined by the type of assignment (e.g., essay, report, case study). However, most assignments have a general structure:
- Title Page: The assignment title, your name, course name, instructor’s name, and date of submission.
- Introduction: Introduce the topic. State the purpose of the assignment. Present thesis statement of your topic or main argument.
- Body: This forms much of your text, which is split into sections or paragraphs dealing with a specific part of the topic. This is structured through effective use of headings and subheadings.
- Conclusion: This gives a general summary of the different points discussed in your text, reiterates the thesis or main argument that is presented in the essay, and concludes the essay with final thoughts or recommendations.
- References/Bibliography: It refers to a list of sources cited in your assignment. Format of References or bibliography should be according to the required citation style.
Format of a university assignment
Formatting is important in ensuring that your assignment meets expected academic standards and information is clearly presented. Here are key formatting guidelines to follow:
- Font and size: The font style should be clear, such as Times New Roman, Arial, or Calibri.
- Margins: Leave a 1-inch (2.54 cm) margin around the entire page.
- Line Spacing: The text body is usually double-spaced while the footnotes and endnotes are single-spaced.
- Page Numbers: These normally appear at the top right corner in the header or footer.
- Header and Footer: Title of your assignment in the header and page numbers at the footer.
- Citations and References: We can use different styles of citation (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) both in-text and in the reference section.
Steps of University Assignment Writing
Make your assignment writing process easy by following these steps:
Understand the Assignment
Clearly interpret what the assignment brief has asked or required of a student. Be certain about the topic, objectives, and criteria that are going to be used for evaluation to guide your work effectively.
Research the Topic
Find relevant and credible sources for information that support the argument. Check the credibility of the source and have organized notes so that one can stretch arguments on a solid base.
Plan and Outline
Design a detailed plan, able to give you the framework of your thoughts and the assignment. This plan should include key areas to be covered, points to be covered, supporting material for the logic in your presentation.
First Draft
Focus on writing the first draft with emphasis on getting ideas across and arguments upfront, without the fear of perfection. Concentrate on placing ideas on paper as they will, at this point, present a preliminary revision or refinement of ideas.
Revise and Edit
Refine your draft for clarity, coherence, and truthfulness. Check for grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and that your arguments naturally flow. Adjust necessary to complete a polished version.
Format and Cite
Make sure your assignment is according to the specified formatting style and citation method. It includes setting right margins, font size, and correctly cited all sources to satisfy academic requirements and avoid plagiarism.
Submit
Finally, review your completed assignment at hand. Check for last-minute errors and ensure that you have adhered to all the requirements. Confirm that everything is in its place, then submit. You should be well-prepared to approach your university assignments and ace them with enhanced skills in academic writing. Be it an essay, report, or any other kind of assignment, a clear vision into formatting, structure, and techniques of writing will help in succeeding at it.
Steps to Write a University Essay
Professional writers of BY Assignment Expert follow the given steps to write a university essay. These steps are:
- Understand the Early: Read the assignment prompt carefully to be clear about the topic, requirements, and the criteria of evaluation.
- Research: Gather all the necessary information from credible sources for arguments.
- Take notes and organize the research material.
- Outline: It gives a framework for the essay by organizing thoughts on the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion.
- Introduction: Start with an attention-grabbing hook, go on to lay the background, and close it with an evident thesis statement.
- Body Paragraphs: Each one should begin with a topic sentence, go on to evidence or examples, then close with a concluding sentence that links the paragraph to your thesis.
- Conclusion: Restate the thesis, summarize major points of the argument, and close with some final thought or call for action.
- Revise and Proofread: Let your essay incubate for a while before re-reading it to check on clarity, coherence and grammatical errors. Remember to cite all sources properly.
Writing a Report for a University Assignment
Reports are formatted differently than an essay and are used to communicate information in a systematic way. Here is a basic example of the format of a report:
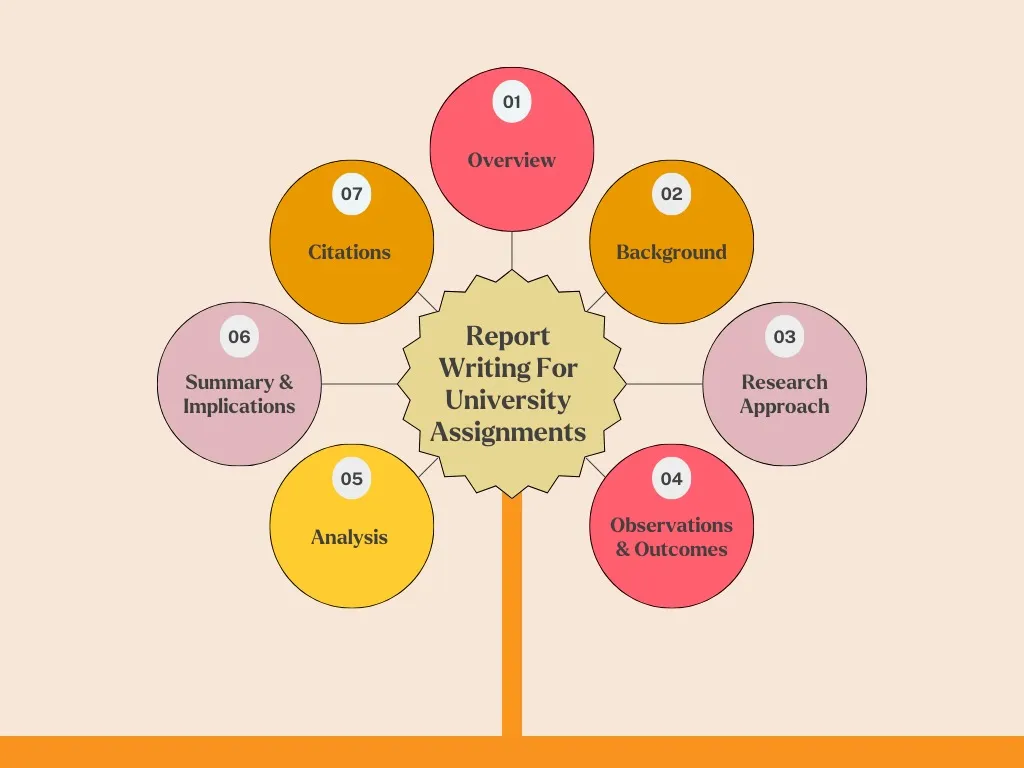
- Abstract: Brief overview of the purpose, method, findings and conclusions of the report.
- Introduction: This section provides the background information, objectives, and scope of the report.
- Methodology: Description of techniques used in collecting data, or how the research was conducted.
- Findings/Results: Information is then presented, or the findings presented in a clear and possibly organized way with the use of tables, graphs, or charts.
- Discussion: Findings are interpreted in relation to the research questions or objectives.
- Conclusion: Summary of key findings and presentation of recommendations or implications of the study.
- References: This is a list of sources that have been used in writing the report.
Tips for writing University Assignments
- Read and interpret the assignment briefly.
- Take detailed notes using relevant sources.
- Getting your thoughts into order with clarity.
- Make a hook, give some context, state your thesis.
- Topic sentences, argue using supporting evidence, and analyze.
- Write main key points and reiterate your thesis statement.
- Be clear, grammatically correct, and appropriately cited. Seek feedback if possible.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in University Assignment Writing
No matter how hard you try doing an exceptional job, there may be some pitfalls to avoid which can compromise your quality work.
- Start Early: Time for planning and to begin the assignment; avoid a rush.
- Effective Time Management: Sufficient time must be allocated to the research, writing, and revision stages.
- Brief Requirements: All parts of the assignment brief are answered. Format and length guidelines must be adhered to.
- Avoid Information Overload: Relevant evidence only; do not include too much information.
- Evidence Consistency: Your evidence must all support your thesis with no contradictory evidence.
- Relevance of Evidence: Evidence should be relevant to your thesis.
- Proofread: Allow some time to proofread your work, identifying and correcting mistakes.
- Check Mistakes: Grammar, spelling, consistency
- Revise Carefully: Revise your work in the light of feedback and self–review
- Address all Assignment Brief Requirements: Ensure all the requirements of the assignment brief are covered in your assignment to obtain the highest marks.
Just following these steps and keeping yourself safe from the dangers can lead to better assignment writing skills and enhanced results. Keep in mind the fact that all it takes is to stay organized and focused with a clear sense of planning ahead of time and attending to the important details. With practice and stick-to-it-iveness, you will develop the confidence and skills to be able to take on any assignment at university and succeed at it.
Examples of Assignment Writing
Following are a few examples which elucidate various university assignments.
- Essay Example: Examine how symbolism contributes to the themes of a chosen literary work. Use examples from the text and scholarly sources to support your analysis. To read samples, you can read a history essay sample regarding antibiotics’ role in medicine history.
- Report Example: A review of how a research paper develops from topic selection down to the final proofreading. In your report, this should take you through all these stages, from research and drafting to editing and formatting, with some suggested best practices for each. For your further clarification, you can read a report on personal effectiveness.
Final Thoughts
This blog gives you one helpful guide through the complexities of university assignments. Following formatting guidelines, properly structuring your work, and keeping clear of common mistakes can strengthen your assignments significantly. It is important to understand the importance of a briefly written assignment, proper research on the topic, and the time to edit and proofread. By engaging in these practices and trying to make a change in your academic writing skills, you’ll be better positioned to boost your performance. Equipped with the strategies outlined in this blog, any assignment can be confidently approached with clarity.